B 2 intracellular sodium ions for 1 extracellular potassium ion. At the normal resting potential of a typical neuron its ion exchange pump A.
Depolarization Hyperpolarization Neuron Action Potentials Article Khan Academy
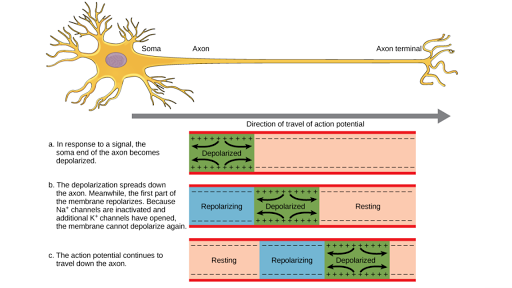
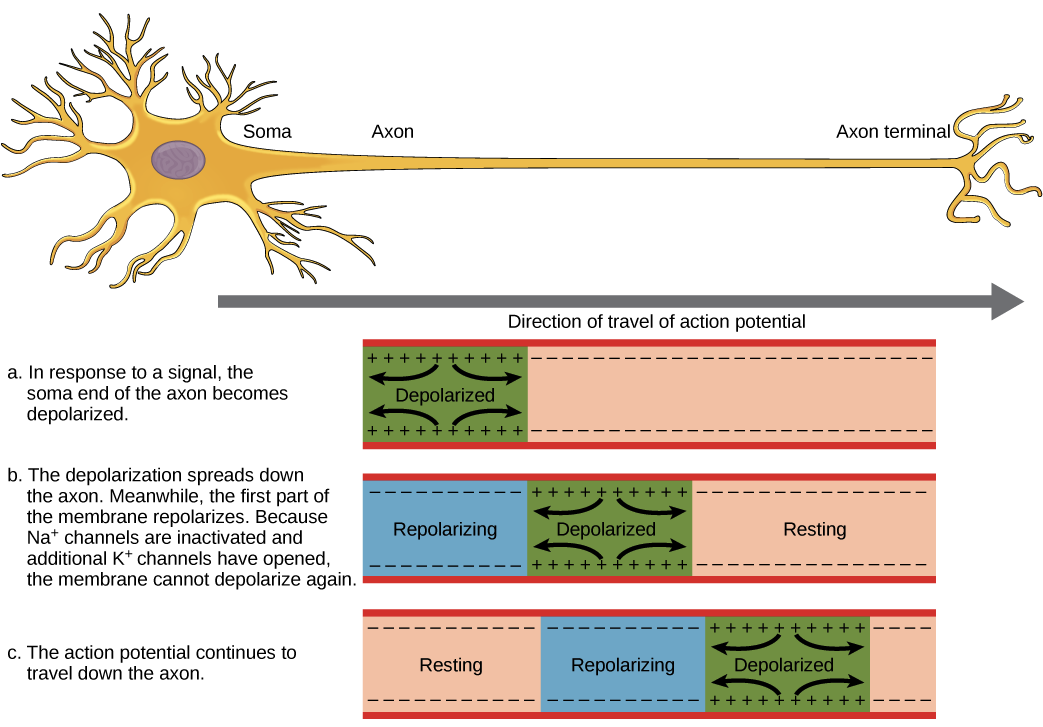
The axon is depolarized when potassium ions diffuses out of it.

. A neuron is said to be polarized because a. C 3 intracellular sodium ions for 1 extracellular potassium ion. What is the expected resting membrane potential in mV of a neuron that is typical in all ways except for possessing an intracellular potassium concentration of 1876 mM and double the normal resting permeability to sodium.
At the normal resting potential of a typical neuron its ion exchange pump. If youre seeing this message it means were having trouble loading external resources on our website. 32 At the normal resting potential of a typical neuron its Na-K ion exchange pump transports A 1 intracellular sodium ion for 2 extracellular potassium ions.
Electrical charge is unevenly distributed between the inside and outside of a neuron with the inside being more negative under normal resting conditions. At the normal resting membrane potential of a typical neuron its sodium-potassium exchange pump transports 3 intracellular sodium ions for 2 extracellular potassium ions. A neuron at rest is negatively charged.
At the normal resting membrane potential of a typical neuron its sodium-potassium exchange pump transports 3 intracellular sodium ions for 2 extracellular potassium ions Ion channels that are always open are called ________ channels. B 2 intracellular sodium ions for 1 extracellular potassium ion. The resting potential of a typical neuron is around -65mV.
Exchanges 2 intracellular sodium ions for 1 extracellular potassium ion. The soma is always at one end of the cell. 59 At the normal resting potential of a typical neuron its sodium - potassium exchange pump transports.
In this article we will discuss the resting potential of a neuron resting potential and action potential and the typical value of. A 2 intracellular sodium ions for 1 extracellular potassium ion. More positive resting potential than normal.
Exchanges 1 intracellular sodium ion for 2 extracellular potassium ions. At the normal resting potential of a typical neuron is na-k ion exchange pump transports University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign BioNeuro 303 Chapter 4 - Study Questions 74. Voltage-gated channels are present.
How might that impact the resting potential compared to that for a typical neuron. Depolarization occurs when potassium ions diffuses into the axon. Similar resting potential as normal neuron.
The resting potential is the normal equilibrium charge difference potential gradient across the neuronal membrane created by the imbalance in sodium potassium and chloride ions inside and. Calcium and Sodium ions are more concentrated on the. MIDTERM Question 1 At the normal resting potential of a typical neuron.
These movements result in different electrostatic charges across the cell membrane. View Test Prep - Nuero FINALdocx from BIO 201 at Salem State University. During an action potential sodium ions diffuse into the axon.
The inside of a cell is approximately 70 millivolts more negative than the outside 70 mV note that this number varies by neuron type and by species. Exchanges 3 intracellular sodium ions for 1 extracellular potassium ion. There c is a difference.
Exchanges 3 intracellular sodium. A 20 kg clock resting on the floor is to be raised by a 50 mm diameter rope with youngs modulus 15 X 109 nM2. D 3 intracellular sodium ions for 2 extracellular potassium ions.
Exchanges 1 intracellular sodium ion for 2 extracellular potassium ions. What would be the approximate equilibrium potential for K using the Nernst equation if K outside the neuron is 1 mM and inside is 100 mM. B 68 At the normal resting membrane potential of a typical neuron its sodium-potassium exchange pump transports A 1 intracellular sodium ion for 2 extracellular potassium ions.
This voltage is called the resting membrane potential. 82 rows At the normal resting potential of a typical neuron its sodium-potassium exchange. Neurons and muscle cells are excitable such that these cell types.
How the resting membrane potential is established in a neuron. At the normal resting membrane potential of a typical neuron its sodium-potassium exchange pump transports asked Aug 6 2017 in Anatomy Physiology by Hiroshima A 1 intracellular sodium ion for 2 extracellular potassium ions. Exchanges 2 intracellular sodium ions for 1 extracellular potassium ion.
C 3 intracellular sodium ions for 1 extracellular potassium ion. When there is resting potential the outside of the axon is negative relative to the inside. The action potential can travel in only one direction.
The resting membrane potential is the result of the movement of several different ion species through various ion channels and transporters uniporters cotransporters and pumps in the plasma membrane. If youre behind a web filter. It is caused by differences in the concentrations of ions inside and.
B 3 intracellular sodium ions for 1 extracellular potassium ion. C 1 intracellular sodium ion for 2 extracellular potassium ions. You hold the at a point 15 m above the flow and pull hard enough to lift the block just off the floor.
The reason for this difference is the distribution of ions across the membrane. The rope goes up and over a pulley that is 25 m above the floor. The resting membrane potential value or a typical value of resting membrane potential is from 60 to 95 millivolts where 1 millivolt 0001 volts and the inside of the cell remains negatively charged.
How the resting membrane potential is established in a neuron.

Neuron Action Potential Sequence Of Events
Depolarization Hyperpolarization Neuron Action Potentials Article Khan Academy

Neuron Action Potentials The Creation Of A Brain Signal Article Khan Academy
0 Comments